Dental imaging software is a core technology used in dental practices to capture, store, and view X-rays and other images. Recent advances have moved these systems from traditional, on-premise installations to the cloud. This shift affects how dental teams access and manage clinical images throughout the day.
Additionally, the global dental imaging market is projected to reach USD 6.42 billion by 2034, providing broader context for these dental trends.
Cloud-based solutions differ in fundamental ways from older dental imaging software models. Understanding these differences is important for dental professionals who want to select the right platform for their practice. The following section explains what cloud-based dental imaging software is and how it works.
Explore Overjet's Dental AI Software
What Is Cloud-Based Dental Imaging Software?
Cloud-based dental imaging software stores and manages dental images using internet servers instead of local computers in your office. You can view, share, and analyze images from any device with web access without depending on a single office computer.
Traditional dental imaging software runs on local servers that require manual updates and on-site maintenance. Cloud-based platforms offer web-based functionality and automatic updates. Your practice maintains access to the latest versions and security features without extra effort.
Key features include:
Remote access: View dental images from any internet-enabled device
Web-based viewer: Handle X-rays, 3D images, and CBCT scans through a browser
Automatic updates: Receive software updates and security patches without manual work
Centralized storage: Store images with encrypted backup in secure data centers
System integration: Connect with practice management systems and digital sensors
Access controls: Assign user permissions based on staff roles
These features allow dental teams to manage images and workflows from different locations, supporting both in-office and remote collaboration.
Cloud vs. On-Premise Imaging Key Differences
Cloud-based systems use the internet to access software and store images on remote servers. On-premise systems store images and run software locally on computers or servers inside your dental office.
Cloud-based software requires only devices with internet access. On-premise software depends on in-house infrastructure, including physical servers, backup equipment, and local networks. On-premise systems may require in-person IT support for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Accessibility differs between these models. Cloud-based software allows you to view dental images from any web-enabled device, whether in the office or off-site. On-premise software usually limits access to computers connected to the local network.
Key Factor | Cloud-Based Imaging | On-Premise Imaging |
Infrastructure | Internet connection and web device | Local servers and network equipment |
Accessibility | Web browser from any location | Office computers on local network |
Maintenance | Automatic updates by provider | Manual updates and on-site IT staff |
Upfront Cost | Monthly subscription fee | High initial purchase and setup cost |
Scalability | Easily adds users or locations | Requires hardware upgrades for scaling |
Clinical Benefits of AI Diagnostics and 3D CBCT in the Cloud
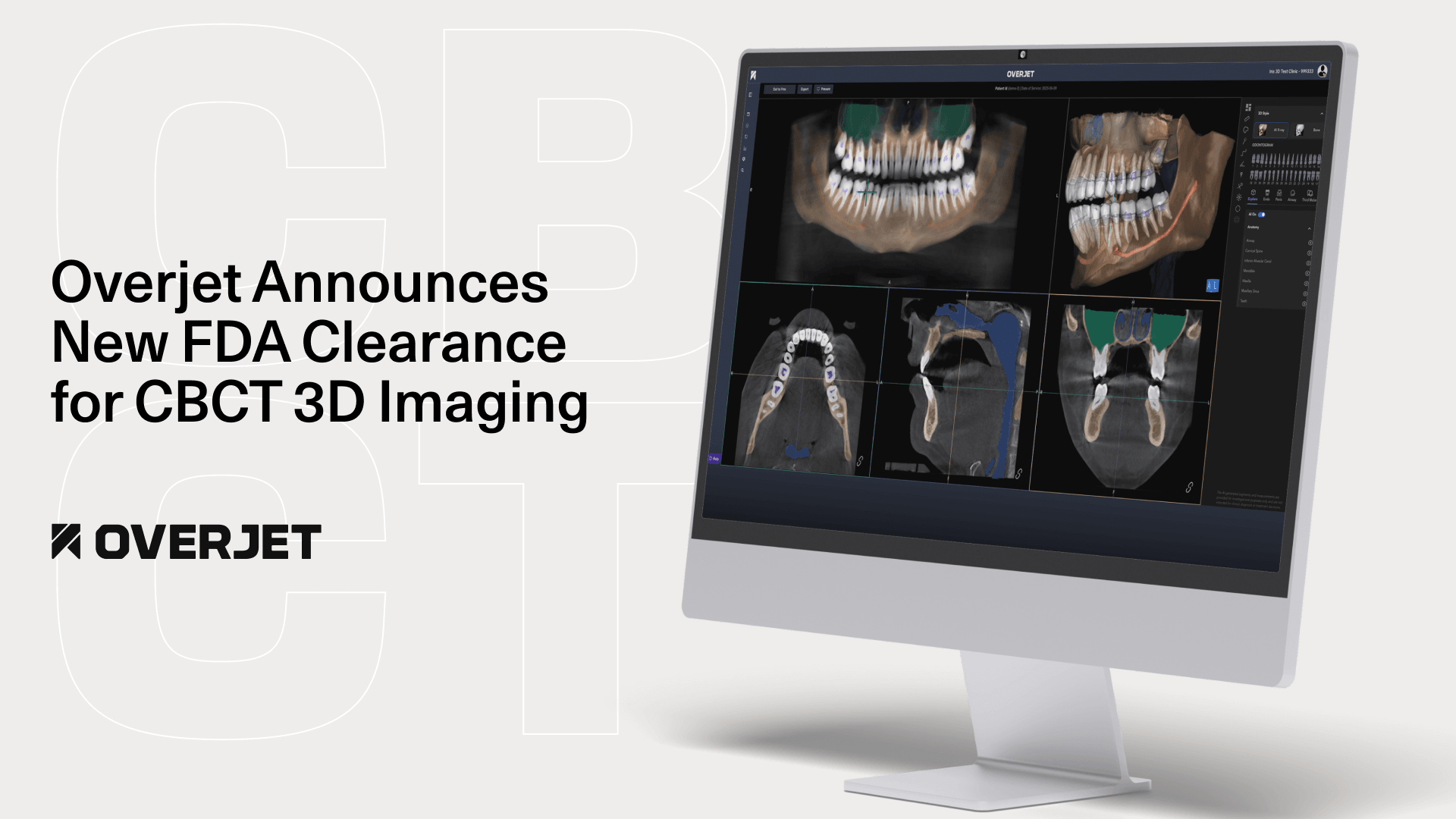
Artificial intelligence in cloud-based dental imaging software analyzes dental X-rays and 3D scans to help identify oral conditions such as cavities and bone loss. AI algorithms recognize patterns in radiographs, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans, and other dental images.
Recent innovations include the University of Hong Kong’s GUM AI mobile health dental software, which has demonstrated over 90% accuracy in dental diagnostics.
Automated caries detection scans dental images and highlights areas that may show signs of decay. This process provides consistent analysis across different patient cases and helps standardize the review of diagnostic images.
For treatment planning, AI uses data from multiple sources to offer suggestions based on patient clinical findings, previous records, and current images. Predictive analytics uses historical and real-time data to estimate the likelihood of future dental issues or outcomes.
Overjet’s FDA-cleared dental AI capabilities support comprehensive diagnosis by providing precise measurements and visual annotations directly on 2D and 3D images, including CBCT scans. This technology works within cloud-based systems to assist dental professionals in making informed clinical decisions.
Security and HIPAA Compliance Requirements
Cloud-based dental imaging software uses several security features to protect patient information. Data encryption converts stored and transmitted data into a coded format so unauthorized people cannot read it. Access controls limit who can view, change, or delete patient data by assigning permissions based on user roles.
HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets rules for handling protected health information in the United States. Dental practices using cloud imaging software follow HIPAA guidelines to avoid unauthorized access or data breaches.
Essential compliance requirements include:
Data encryption: Protect all patient data during storage and transmission
User authentication: Require unique logins and strong passwords for every user
Role-based permissions: Give staff access only to information needed for their job
Audit trails: Track user activity on patient records for compliance checks
Secure backups: Maintain regular data backups in offsite locations
Business Associate Agreements: Sign contracts with vendors that handle patient data
Integration With Practice Management and Insurance Platforms
Cloud-based dental imaging software connects with other digital tools used in dental practices. This includes systems for managing appointments and billing (practice management systems), electronic health records (EHR), and imaging hardware such as digital X-ray sensors and intraoral cameras.
Software providers use application programming interfaces (APIs). An API is a set of rules that allows different software programs to share information and work together. With APIs, dental imaging software exchanges data with practice management and EHR systems in real time.
Some platforms connect directly to imaging sensors and hardware. Images are automatically uploaded to the cloud software without manual steps. Workflow automation happens when tasks like attaching X-rays to claims or syncing patient data with billing systems occur in the background.
Overjet integrates with multiple practice management systems, allowing practices to use their existing software alongside AI-powered imaging and analytics. This approach supports continuity and helps dental teams manage data from imaging, scheduling, and insurance workflows in one connected environment.
Total Cost of Ownership and Pricing Models
Cloud-based dental imaging software uses subscription-based pricing, while traditional on-premise solutions typically require an upfront investment. Subscription pricing is billed monthly or annually and often covers software access, storage, updates, and technical support.
When comparing pricing structures, consider these factors:
Upfront cost: Subscription pricing has low or no upfront fees; on-premise systems require substantial payment at the start
Ongoing expenses: Subscription plans include regular payments; on-premise systems may require annual support contracts and IT labor fees
Updates: Cloud subscriptions include automatic updates; on-premise software may charge for version upgrades
Hardware requirements: Cloud software works with standard internet-connected devices; on-premise solutions may require servers and backup equipment
Hidden fees: Possible extra charges include data migration, storage beyond plan limits, or training
5 Questions to Ask Vendors Before You Buy
Selecting cloud-based dental imaging software often involves comparing several vendors. Asking targeted questions clarifies key differences between platforms, especially when evaluating technologies that use artificial intelligence or connect with other systems in the dental office.
1. What Is Your Uptime and SLA?
Ask about their guaranteed uptime percentage, which shows how often the system is available and working as expected. Find out if the vendor provides a service level agreement (SLA) that outlines what happens if downtime occurs, including any compensation for extended outages.
2. How Do You Handle Data Migration and Backups?
Ask how the vendor manages moving data from your current system to the new software. Find out how often the system backs up your data, and ask about their disaster recovery protocols if there is a system failure or security incident.
3. Which AI Features Are FDA-Cleared and Continuously Updated?
Ask which artificial intelligence features have received clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Ask how frequently the vendor updates its AI models and whether improvements are released to all users. Overjet’s platform includes FDA-cleared dental AI solutions that are updated to maintain compliance and accuracy.
In addition to Overjet, several other companies have achieved significant FDA clearances in dental AI imaging:
Pearl’s Second Opinion®: The first FDA-cleared AI radiologic detection aid for dental conditions.
VideaHealth: Received FDA 510(k) clearance for Videa Dental AI with more than 30 AI algorithms, making it the first dental AI company offering insights for virtually every disease state in dentistry.
Auto-Chart: The first and currently only dental auto-charting product cleared by the FDA.
DentalMonitoring: Received De Novo approval, becoming the first AI-enabled dental software to receive De Novo approval from the FDA.
These recent FDA clearances provide dental professionals with a broader range of validated AI options to consider when evaluating platforms.
4. Can You Demonstrate Seamless Integration?
Request a live demonstration of how the software integrates with practice management systems and digital sensors. Ask to see workflow automation capabilities and observe how data moves between systems during everyday tasks.
5. What Is the Complete Monthly Cost at My Practice Volume?
Ask for a breakdown of the monthly cost based on your expected number of users, imaging volume, and locations. Request details about all fees, user limits, storage caps, and any volume-based pricing tiers to understand the total cost of ownership.
How to Evaluate FDA Clearances and Validation Studies
Regulatory approval, such as clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), determines if medical device software meets established safety and effectiveness standards. For dental AI software, FDA clearance is based on a review of technical documentation, performance data, and clinical evidence.
Clinical validation refers to studies that test the AI algorithm’s accuracy and reliability using real-world data. These studies usually compare the AI’s findings with those of experienced dental professionals or with a known clinical standard.
To verify the effectiveness of an AI algorithm, reviewers can request validation studies that detail how the software was tested. Key information includes the size and diversity of the dataset, the clinical scenarios covered, and the statistical outcomes. This information is often available in FDA databases, peer-reviewed journals, or on the software provider’s website.
Action Plan to Implement Cloud AI Imaging in Your Practice
An organized approach helps practices transition to cloud AI dental imaging. Each step addresses a key area of technology change, from equipment checks to ongoing monitoring.
Step 1: Audit Current Hardware and Workflows
List all existing imaging devices and examine their compatibility with cloud-based AI software. Identify any steps in current imaging workflows that are slow, manual, or prone to error.
Step 2: Shortlist Vendors and Request Demos
Develop a set of requirements based on clinical, administrative, and technical needs. Use these criteria to narrow down the list of possible software vendors and request live demonstrations of each platform.
Step 3: Conduct Security and Compliance Review
Review each vendor’s approach to data security, including encryption and access controls. Examine whether the platform follows HIPAA requirements and how it manages data protection.
Step 4: Pilot Program and Staff Training
Select a small group of users and run a trial of the new software. Provide targeted training for staff and observe how the new system fits into day-to-day routines.
Step 5: Full Rollout and Performance Monitoring
Deploy the software across the full organization. Track specific metrics such as staff adoption, imaging turnaround times, and system reliability to monitor success and address issues as they arise.
Elevate Patient Care With Overjet AI Imaging Solutions
Overjet offers a platform that uses artificial intelligence to help dental professionals detect and measure oral conditions on dental images with high accuracy. The software provides clear, annotated visuals that show where issues such as cavities or bone loss may be present.
The platform includes educational tools that display findings in a way that is easy to follow. This allows dental teams to explain diagnoses and treatment recommendations using the same images and data analyzed by the AI.
For dental insurers and administrators, Overjet automates several tasks related to insurance claims. The system verifies patient eligibility, assists with credentialing, and reviews claims using AI, helping to reduce manual work and speed up processing times.
Ready to See Overjet's Dental AI in Action?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How much does data export cost when switching cloud imaging vendors?
Most vendors charge a fee for exporting data based on storage volume, though some include migration support at no extra cost. Review contract terms carefully to understand potential switching costs before signing.
What uptime percentage guarantees reliable cloud dental imaging access?
Industry standard is 99.9% uptime with financial penalties for extended downtime. Service level agreements often specify compensation if the system is unavailable beyond the agreed threshold.
How do cloud imaging systems document AI findings for insurance claim reviews?
Cloud-based systems provide audit trails and annotated images that display AI analysis results. These systems generate documentation showing AI-identified findings that can be referenced during insurance audits and claim reviews.